

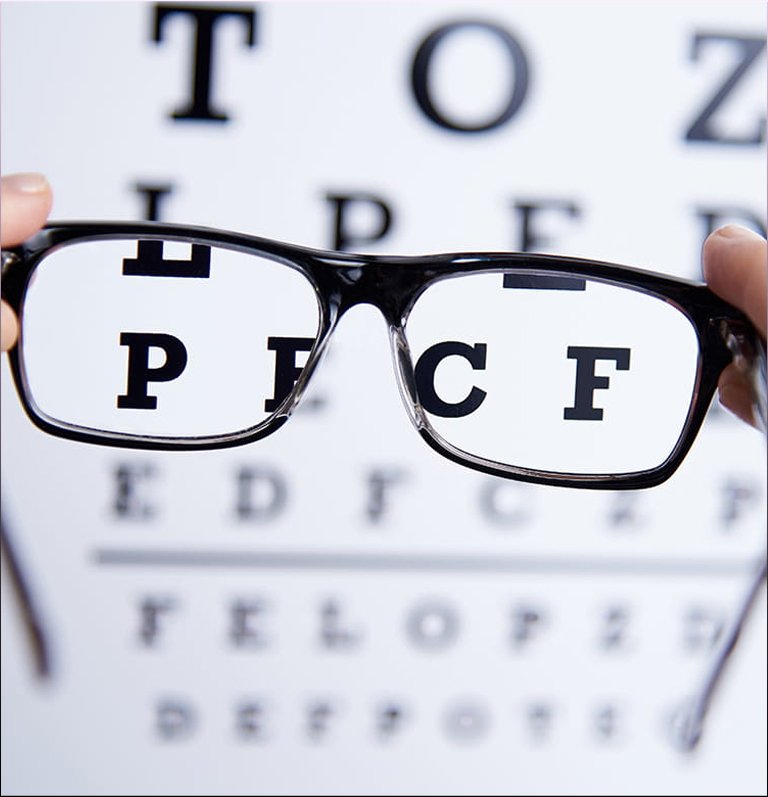
Low vision refers to a visual impairment that cannot be fully corrected by glasses, contact lenses, medication, or surgery, and significantly impacts a person's ability to perform daily activities. Unlike total blindness, individuals with low vision still retain some degree of sight, but it is often blurred, limited, or distorted. This condition can result from various eye diseases, congenital conditions, or injuries.
People with low vision experience difficulties with tasks such as reading, writing, driving, recognizing faces, and navigating their surroundings. They may require assistance and adaptive aids to compensate for their reduced vision, such as magnifiers, large-print materials, or screen-reading software.
The causes of low vision are diverse and can include age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, cataracts, retinitis pigmentosa, and congenital disorders like albinism or optic nerve hypoplasia. Each condition manifests differently and affects visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, peripheral vision, or color perception to varying degrees.
Living with low vision can have significant impacts on an individual's independence, emotional well-being, and quality of life. It may necessitate adjustments in lifestyle, employment, and recreational activities to accommodate visual limitations. Rehabilitation services, including vision therapy, orientation and mobility training, and counseling, can help individuals with low vision maximize their remaining sight and regain confidence in performing daily tasks.
Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals is crucial in helping individuals with low vision adapt to their condition and maintain an active and fulfilling life. Through a combination of adaptive strategies, assistive technologies, and community resources, people with low vision can overcome challenges and participate fully in society.
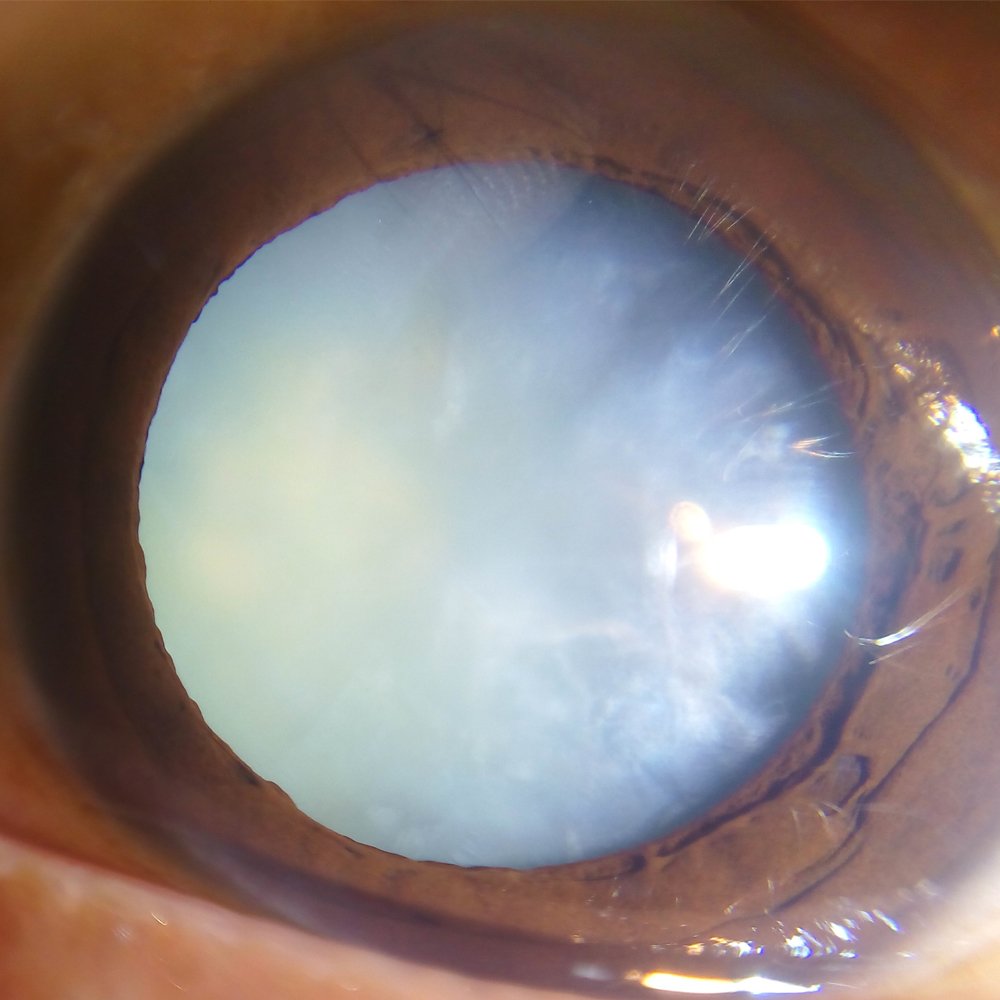
You can protect your eye health and potentially slow the process of cataracts by: Not smoking, Protecting your eyes from the sun, Getting regular eye care, and Wearing sunglasses and a hat with a brim to block ultraviolet sunlight.
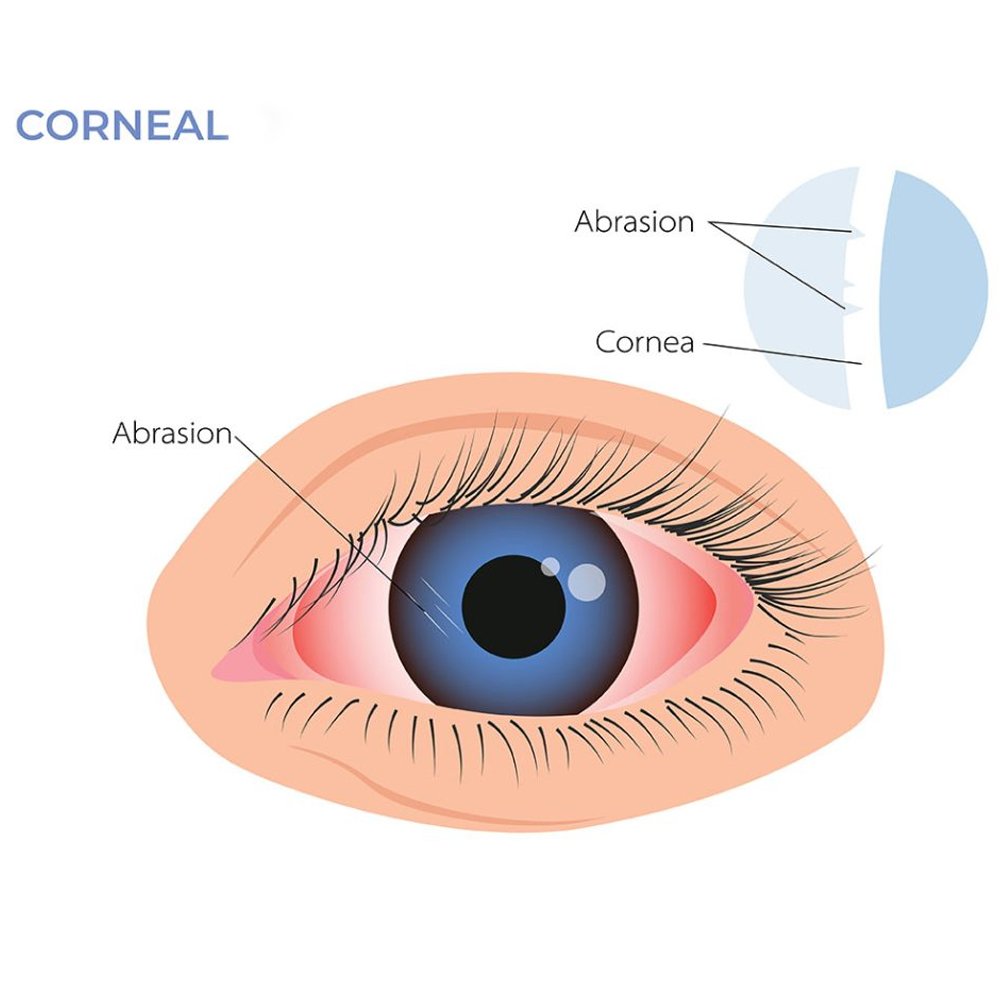
Corneal disease, also known as ocular surface disease, is a group of serious conditions that can affect the cornea. These conditions can cause the cornea to become distorted, clouded, or scarred, and can even lead to blindness.
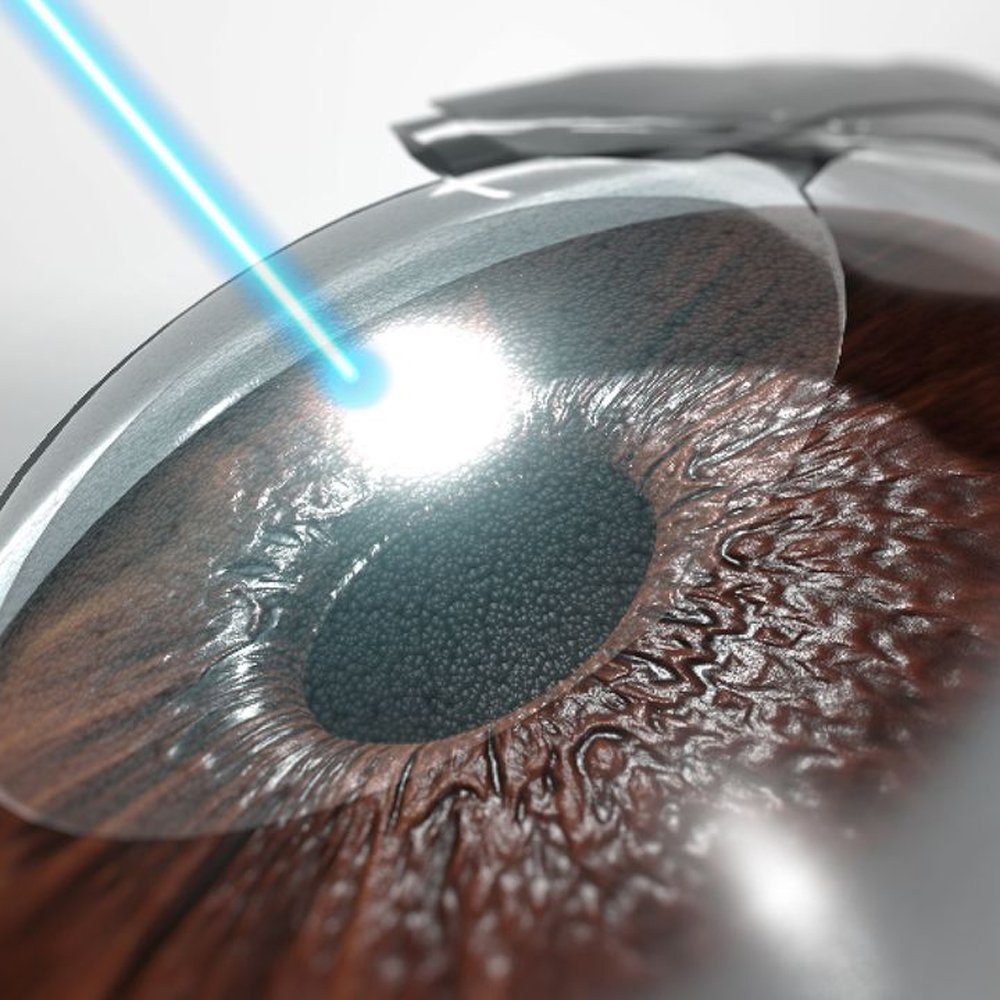
Refractive surgery is an optional eye procedure that improves the eye's refractive state and can reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses . It can involve reshaping the cornea, implanting a lens, or replacing the lens.

The retina is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that receives light and converts it into chemical energy. The uvea is the middle layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera (white part of the eye). The uvea is made up of three parts !

Emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat milk and milk products.

There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, the majority have suffered alteration

There are many variations of passages of Lorem Ipsum available, the majority have suffered alteration
Refractive surgery can correct refractive errors like nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, or presbyopia. Some of these surgeries reshape the cornea. Others implant a lens in your eye. Either way, the goal is the same. These surgeries focus light correctly on the retina so you can see more clearly.
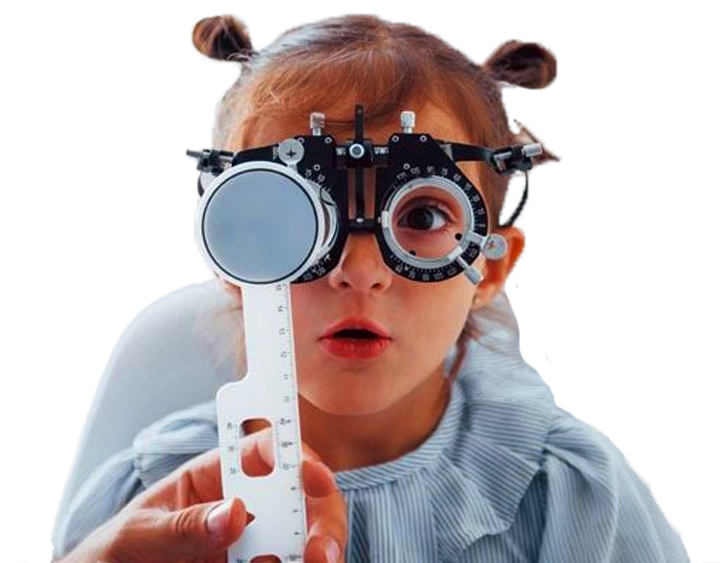


Pediatric ophthalmology is a subspecialty of ophthalmology that concentrates on treating the various eye problems affecting children. Studies show that a lot of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and learning issues in children can be attributed to vision problems.